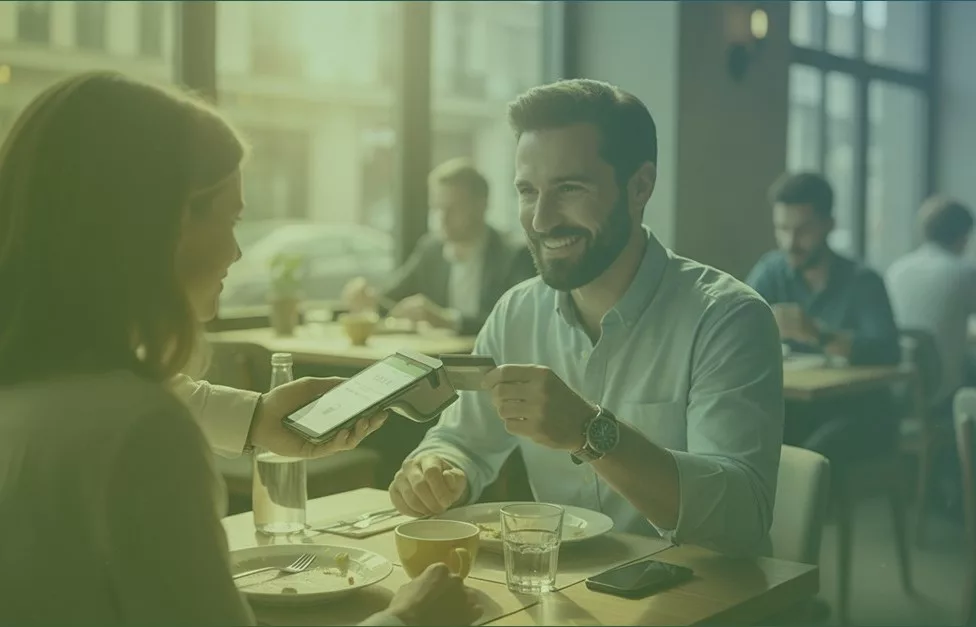
“I’m a regular customer at several online stores and I want to make sure my bank card details are not going to be stolen or duplicated.”
You need to keep your account number (PAN) and other sensitive card details protected.
“Sure, and how do I do that?”
- Well, this should be taken care of by the merchant itself through a card tokenization tool. That is a system that allows you to replace sensitive data with non-sensitive data called tokens.
- “And how does it work?”
- The tokenization system receives sensitive data. This data is centrally stored and protected with strong encryption. Next, the tokenization system generates a unique token and associates it with the previously stored data. Finally, the token is put into the application’s operational flow and replaces the sensitive data in all operations.
“Interesting!”
Read on and we’ll explain how companies add maximum security to their card transactions. Will you join us?
The token on cards – what is it?
A token in the payments ecosystem is a digital asset that replaces sensitive data. It is synonymous with trust and security. It is a kind of substitute for your sensitive data to ensure its protection during transactions.
It is part of the card tokenization process, which involves converting your customers’ card data into encrypted tokens. It applies to data security and replaces a sensitive data element with a non-sensitive equivalent called a token. It has no extrinsic meaning or value.
The process is as follows:
- The system receives confidential data. Depending on the interfaces, the data is retrieved, imported or entered by a user.
- The sensitive data is replaced by a token or strong encryption code. That is, the account number, or any other data, is not stored, but a substitute for it. The actual customer data is only available to the bank; what we receive from the bank is a token. We store it and it allows us to make the customer’s payment experience faster and more secure.
- The token is unique and associated with the previously stored sensitive data. This will serve as an alias to the actual data.
- The token is put into the operational flow and replaces the sensitive information it represents in all transactions.
In three words, the process consists of provisioning (the client has a token linked to their PAN or Personal Account Number), validating (the token is sent to the credit card network to process the transaction), and authorising (when the validation of the operation is received, the network tokenises the data and sends the authorisation to the seller).
The tokenization system enables secure encryption of your customers’ card details, and even faster online payment experience, saving time when receiving payments and settling payments in a single click.
Buying securely has never been easier!
Tokenization and PCI DSS
Are you looking for maximum security for your payments or would you just like to improve your customers’ experience? Then, you should think about including card tokenization in your payment processing. The management and storage of sensitive information is a matter of great concern for any business today.
That is why the PCI DSS regulation was created, which is responsible for regulating the management and storage of data associated with payment cards. This regulation includes tokenization techniques within the PAN’s protection methods, which can be protected with an associated token based on different patterns:
- Full replacement with number string and letters. The token can have a different format than the data it replaces and is usually the most challenging to manage, since it requires some modifications to the associated databases.
- Full replacement with a token of the same length and format. It has minimal impact on any associated system.
- Partial replacement, keeping the first and last positions the same. Average data is replaced with a token. A differentiation technique between PAN and token is required to prevent data from being contaminated in this model.
However, tokenization is not the only alternative to card protection, as the PCI DSS ecosystem establishes different strategies to protect the PAN when it needs to be stored. These methods are: tokenization, strong cryptography, truncation, and one-way hash values.
The PCI DSS states its scope as follows: “The primary account number is the defining factor for the applicability of the PCI DSS requirements, which apply if you store, process, or transmit a primary account number (PAN). If a PAN is not stored, processed, or transmitted, PCI DSS requirements do not apply…”
When should I proceed with tokenization and how do I comply with the regulations?
We must bear in mind that a token is not a PAN, but a substitute for it. Therefore, the PCI DSS requirements do not apply where it is stored, processed or transmitted. The business processes through which a token flows are not subject to compliance with the standard. In contrast, those systems that interact with payment card data are within the compliance framework. What requirements must be met?
- The tokenization system used must not provide the number to any network or user outside the scope of compliance.
- The card token must use strong cryptography algorithms.
- The tokenization tool must implement access controls and authentication measures.
- All components of the tokenization system must be located on a secure internal network.
Do you understand what tokenization is? Do you know what the token on the card consists of? Do you have any questions about how it works? How does it fit into your business?
At PayXpert, we answer all your questions.