In this post we will give an overview on the common types of chargebacks, so it will be possible to understand the origin of the loss and take remedies to minimize them. Merchants need to pay special attention to the chargeback they receive to better understand the business they are running.
Each chargeback is marked by a numeric code that is commonly know as the reason code. Reason codes are used by Brands to categorize the cause why the transaction has been rejected by the customer. With the reason code the Merchant receive the first information on error occurred. Starting with the reason code it will possible to characterize which type of chargeback the Merchant is facing
The following are the most common types of chargebacks that Merchant may face:
MERCHANT ERROR:
In the previous posts we have analyzed two aspects related that Merchant need to take into the account to run their business online. In the first one we have highlighted the requirements they have to meet to have a website fully compliant. In the second post we have suggested tips to Merchants to reduce the possibility to reduce chargeback due to errors they may cause when dealing with their customers.
Merchant Error may represent up to the 30% of the total chargebacks and the origin of the chargeback is because the Merchant did not fulfill the promise made or has been unable to satisfy customer’s need.
These chargebacks can be filled as a consequence of:
- The merchant did not provide the product or service as described
- The client never received the product
- The client received the product damaged or in not perfect condition
- The customer was charged wrongly
- The customer was not able to reach an agreement with the Merchant regarding exchanges or refund request
In this case the Merchants will receive chargeback with the following reason codes:
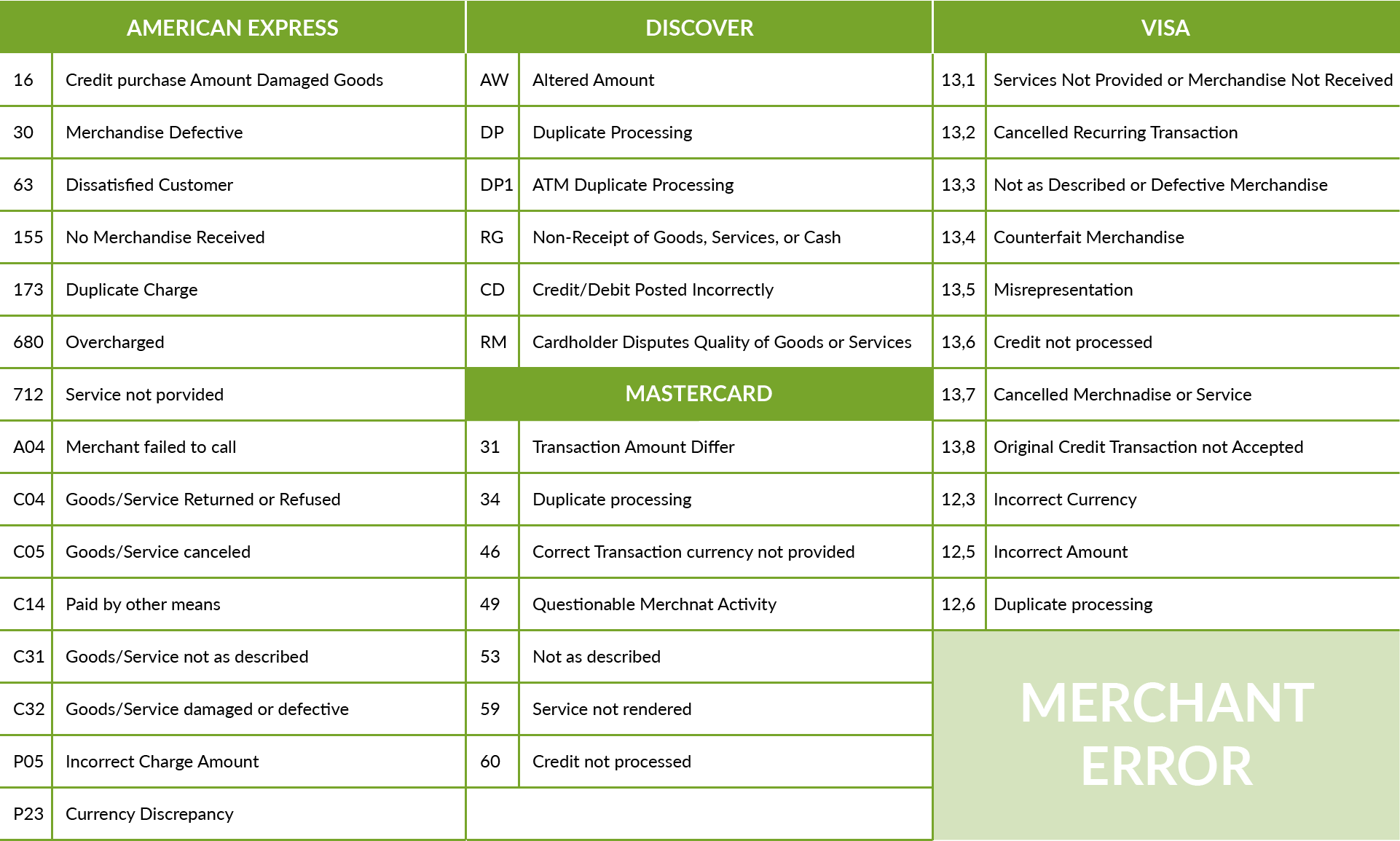
This kind of legitimate chargebacks can be prevented by offering an outstanding customer service to handle customer’s queries, having flexible return or refund policies and a website with a clear description of the goods or services offered and clear definition of the prices.
CRIMINAL FRAUD:
The second common type of chargebacks is due to credit card fraud. When cardholders find illegitimate charges on their bank or credit statements that they know they did not authorize, they are made aware that their card has been compromised. If the customer is sure that they did not make the specified purchase, they then can contact their issuing bank and inquire about the charges. This typology of fraud may represent up to 10% of all chargebacks of the Merchants.
In this case the Merchants will receive chargeback with the following reason codes:
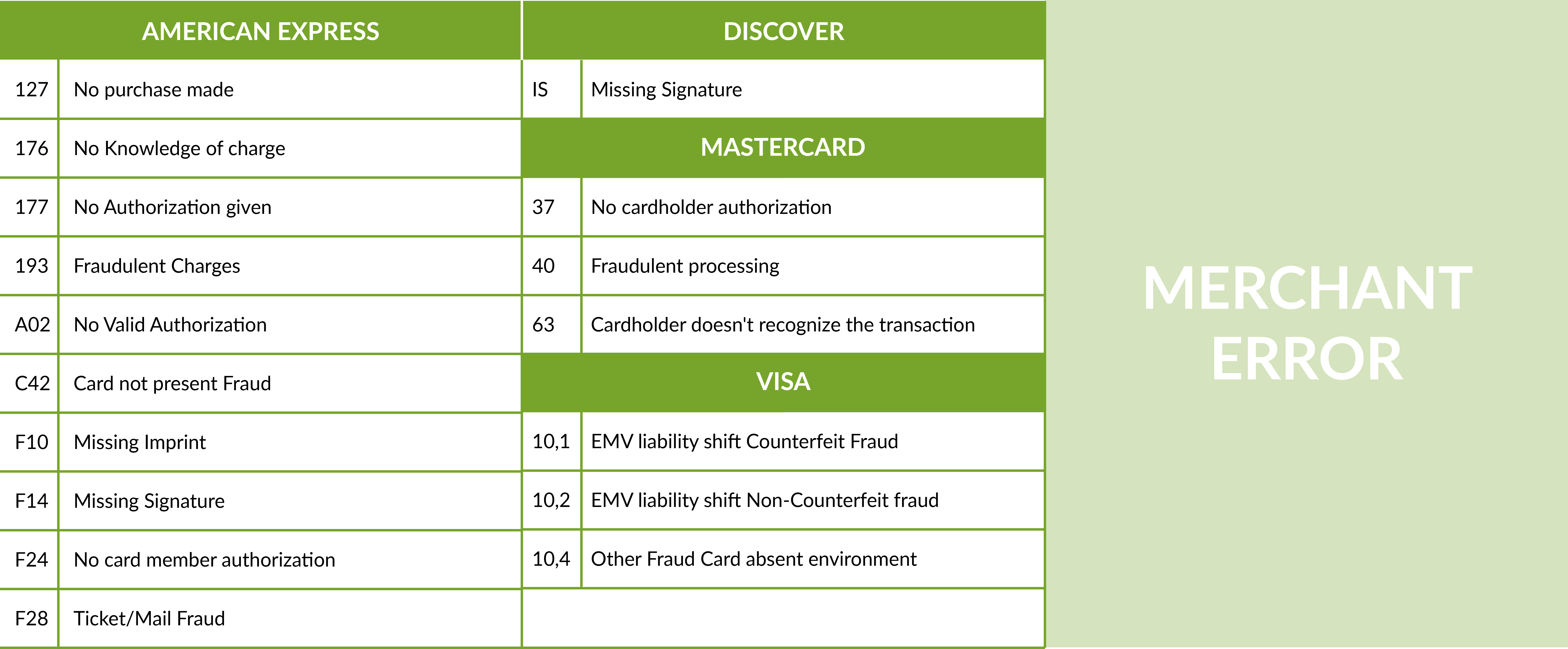
To prevent chargeback coming from criminal fraud Merchant need to establish a well structured plan that include the introduction of best practices (like the introduction of AVS verification, 3D Secure, CVV number) and choose the right payment processing solution with strong antifraud engine that will be able to manage complex real time data, have a top class fraud screening and analytics and set up tailored chargeback alerts.
FRIENDLY FRAUD:
Although this may refer to something amicable, there is nothing nice about friendly fraud and in fact the impact of the friendly fraud is by far the most common type of chargebacks that Merchants receive and can reach level of 60-80% of all of them.
Is quite normal in each business to have dissatisfied customers but the majority of them will contact the Merchant and will try to find a solution for their dissatisfaction. In this case the Merchant should use all the measures they have to understand the nature of the customer complaint (maybe the disappointment is real or maybe not, maybe the goods or service provide can be improved or not, maybe a some stage a misunderstanding occurred or maybe not etc).
Most of the times, on the other side, customers will abuse of their right to file a chargeback and will twist the process with the intent of taking advantage of the situation. In most of the cases the friendly fraud is a consequence of purchase that has been made, authorized, shipped and received with no problem at all and surprisingly enough they will have their money back and maintain also the product and the Merchant is left licking his wounds.
In this case Merchant will receive chargebacks with reason codes that will be either from the Merchant error list (i.e- Service not as described) or from the Criminal fraud one (i.e- No cardholder authorization).
Friendly fraud is probably the most difficult to fight because the Merchant did everything correctly in the first place but then need to invest time and money to demonstrate the transaction legitimacy: in this case the Merchant should use the so-called “compelling evidences” to demonstrate the transaction genuineness. Compelling evidence (like delivery tracking with reference of reception, geo-locatization information, use of previous similar transactions delivered with no issue etc) will help the Merchant to build and present to their banking partner a solid case and increase the chance of a positive resolution.